Understanding Proctitis
Understanding Proctitis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
Proctitis is one such condition. Often misunderstood or simply unheard of, it can significantly impact quality of life. Let's see what proctitis is, its tell-tale signs, what causes it, and how it can be effectively managed.
What Exactly is Proctitis?
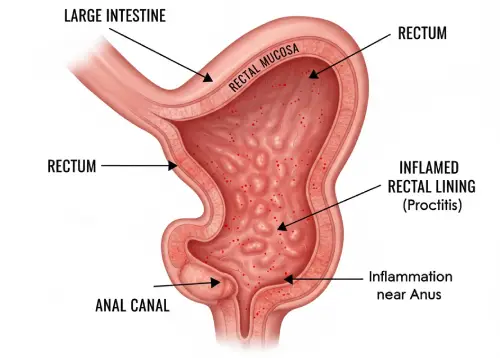
In simple terms, proctitis refers to inflammation of the lining of the rectum, the final section of the large intestine that connects to the anus. While it might sound intimidating, understanding its nature is the first step toward relief. This inflammation can lead to a variety of uncomfortable symptoms, and recognizing them is crucial for a timely diagnosis.
Proctitis Symptoms
One of the most characteristic symptoms of proctitis is tenesmus. This is the persistent, often painful, feeling that you need to pass stool, even if your bowels are empty. It can be incredibly frustrating and disruptive. Beyond tenesmus, other common symptoms include:
-
1. Rectal bleeding :
- This can manifest as bright red blood on toilet paper, in your stool, or dripping into the toilet bowl.
-
2. Rectal pain :
- Discomfort or aching in the rectal or anal area.
-
3. An urgent need to defecate :
- A sudden, compelling urge that can be difficult to control.
-
4. Diarrhea :
- Frequent, loose stools.
-
5. Passage of mucus or pus :
- Sometimes, you might notice discharge.
-
6. Pain during bowel movements.
-
7. Constipation :
- In some cases, proctitis can also lead to difficulty passing stool.
-
8. Inflammation near anus :
- This refers to the proximity of the inflammation, which can sometimes cause external discomfort or tenderness.
If you're experiencing any of these, especially persistent tenesmus or rectal bleeding, it's crucial to seek medical advice promptly.
What are the Common Proctitis Causes?
The origins of proctitis can be varied, and pinpointing the specific cause is key to effective treatment. Some of the most common culprits include:
-
1. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) :
- Conditions like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis can cause inflammation anywhere in the digestive tract, and the rectum is a frequent target.
-
2. Infections :
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as herpes, gonorrhea, and chlamydia can lead to proctitis. Other infections from bacteria like Salmonella, Shigella, or Campylobacter can also be a cause.
-
3. Radiation Therapy :
- Patients undergoing radiation treatment for cancers in the pelvic area (e.g., prostate, rectal, cervical cancer) can develop radiation proctitis, sometimes years after treatment.
-
4. Antibiotic-associated Proctitis :
- Certain antibiotics can disrupt the normal gut flora, leading to an overgrowth of harmful bacteria like Clostridium difficile, which can cause inflammation.
-
5. Food-induced Proctitis :
- In some instances, certain foods might trigger an inflammatory response in sensitive individuals.
-
6. Diversion Proctitis :
- This can occur in people who have had colostomy or ileostomy surgery, where a section of the bowel is "diverted" and not used for stool passage.
-
7. Ischemic Proctitis :
- This is less common and results from a lack of blood supply to the rectum.
Understanding these varied proctitis causes is vital for your doctor to conduct the right diagnostic tests.
Treatment Options: Finding Relief
The good news is that proctitis is often treatable, and the approach depends heavily on the underlying cause.
-
For infectious proctitis :
- ✅ Antibiotics, antivirals, or antifungals will be prescribed to target the specific pathogen.
-
For IBD-related proctitis :
- ✅ Anti-inflammatory medications, such as oral corticosteroids, topical steroids (enemas or suppositories), or immunomodulatory, are typically used to control the inflammation. Biologic therapies may also be an option for severe cases.
-
For radiation proctitis :
- ✅ Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and may include anti-inflammatory medications, sucralfate enemas, or even endoscopic procedures like argon plasma coagulation for bleeding
-
For antibiotic-associated proctitis :
- ✅ Discontinuing the offending antibiotic and treating the C. difficile infection (if present) are key.
-
Dietary and lifestyle adjustments :
- ✅ Sometimes, dietary changes can help manage symptoms, especially for mild cases or when food triggers are suspected. Avoiding irritating foods and increasing fiber intake can be beneficial.
-
Symptomatic relief :
- ✅ Over-the-counter pain relievers and sitz baths can help alleviate discomfort.
